Many companies know where they want to go, but don't have a clear picture of how to get there. Ideas and goals often go nowhere and are not realized because they lack a clear plan. One management model that can help design actionable and executable plans is OGSM.
This article explains what is the meaning behind these four letters, how the OGSM model works and what OGSM and OKRs have to do with each other.
What to expect:
- What is OGSM? Definition
- The 4 elements of OGSM
- How does the OGSM framework work? 5 steps
- What does the OGSM model offer? Advantages and disadvantages
- OGSM vs. OKR: What is the difference?
- OGSM and OKRs – still a good combination?
- Conclusion: long-term planning with OGSM, short-term flexibility with OKRs
- OGSM model – FAQ
What is OGSM? Definition
The abbreviation “OGSM” stands for “Objectives, Goals, Strategies and Measures”. In combination, these four elements form a world class strategy model and widely used framework that can help companies transform their vision into an actionable business model and strategy.
OGSM helps organizations define what they want to achieve and break down how exactly they will accomplish that goal.
Overarching long-term objectives are identified and translated into clear, measurable goals. It also outlines actionable strategies to achieve those goals and develops measures to track progress toward achieving them.
All of this takes place at the executive level and is shared top-down, along the lines of:
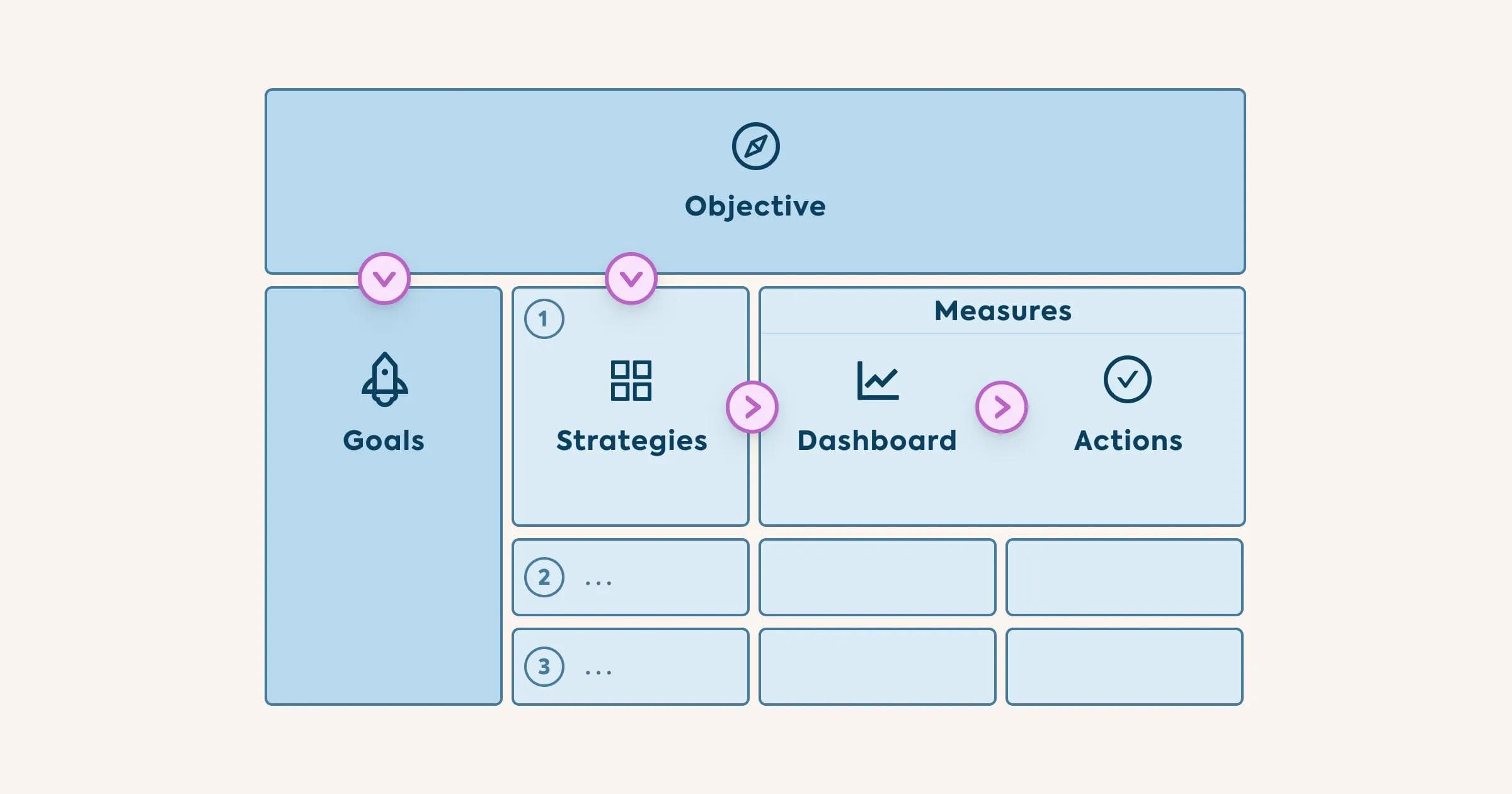
The 4 elements of OGSM
The OGSM model consists of four core elements:
- Objectives are qualitative long-term goals set by management. They are intended to inspire and indicate an organization's vision, i.e. where an organization wants to be in one, three or five years.
- Goals are used to define success. They specify what actually needs to be accomplished in order to meet the desired objective.
- Strategies express how exactly the individual goals are to be achieved and outline who has to do what.
- Measures show how close (or far) one is to achieving the objectives. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to monitor progress and measure success of the strategies.
So, strategy development using the OGSM framework answers the following four questions:
- In what direction is the company moving?
- What will it look like when we get there?
- In what way will we get to the destination?
- How do we know we are on the right track?
How does the OGSM framework work? 5 steps
Although the OGSM model can be broken down to four core elements, its implementation in the organization takes place in five steps:
1. Define the objective
The OGSM planning process always starts by setting an inspiring main objective. The statement describes a company's mission and long term visions. To ensure that all team members understand it, the objective should be formulated as clearly and concisely as possible, and should get to the heart of what is to be achieved and how it is to be achieved.
An example: For an automobile manufacturer, an effective objective statement could read: We will become the global market leader in the production of electric vehicles by focusing on state-of-the-art battery technology, high-performance motors and an innovative mindset.
2. Select goals
Once the main goal is in place, the next step of OGSM defines success. Here, the focus is on what is needed to quantify what success looks like or what results need to be achieved to realize the overall objective. Usually, three to five medium term business goals are defined for this purpose.
💡 Tip: When formulating the goals, make sure that they are as SMART as possible – i.e., specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound. You can read more about how exactly the SMART goals method works on our blog.
3. Develop strategies
The next step is to consider precisely how the goals can be achieved. What specific steps are needed to get to the goal? Again, three to five strategies for each goal should be written down.
Please note: Even though the “S” in OGSM stands for strategies, it means something different at this point than the general term “strategy” in the sense of an overarching plan.
4. Identify measures
The final step in the planning process is to identify and define quantifiable success metrics that can be used to visualize whether the strategies are successful. This usually works through KPIs that measure the success of the strategies within a defined time frame. How these actually look like depends on the strategies that one is trying to implement.
In any case, the metrics should:
- be quantitative and show a trend.
- be easily traceable.
- be accepted as a good metric by all stakeholders.
Depending on whether the assessment then shows that expectations are being met, exceeded, or undercut, strategic planning should be adjusted.
5. Launch actions
The last step is not directly represented by a letter in the model, but it is quite essential when it comes to putting the developed plan into action: To make sure that each team and all employees know what they have to do, it makes sense to break down the strategies even further into concrete actions, identify required resources and define responsibilities.
What does the OGSM model offer? Advantages and disadvantages
The OGSM framework links strategic planning with concrete actions. As such, it offers several advantages:
- ✔️ OGSM results in a clear, simple, one-page plan that is understood at all levels of an organization.
- ✔️ Objectives are directly linked to actions and measures in the OGSM model. This increases the likelihood of actually achieving them.
- ✔️ OGSM is suitable for all types of strategic plans, regardless of the size of the organization, project or team.
At the same time, OGSM does come with some challenges. These are the biggest drawbacks of the framework:
- ❌ OGSM is focused on long-term goals. Short-term changes are often impossible or difficult to make. This makes OGSM less suitable for companies that have to react frequently and quickly to changes (external to the market or within the company).
- ❌ OGSM focuses on the “big picture”. Accordingly, there is a risk that strategies are too broad and that what is really important is not measured.
- ❌ OGSM follows a clear top-down approach and relies on strong leadership. Feedback from employees and course corrections are not provided.
OGSM vs. OKR: What is the difference?
Another management method that also works with clear targets and uses partly similar wording as OGSM is OKR – short for “Objectives and Key Results”.
💡 Tip: If you want to refresh your knowledge of OKRs at this point before moving on, it's best to take a look at our OKR guide.
However, as similar as the terminologies are, the two frameworks function very differently at some points.
Specifically, OKRs and OGSM have the following 🤝 similarities and ⚡ differences:
- 🤝 Focus: Both frameworks specify what is to be achieved and how to get there.
- ⚡ Direction: Goals, strategies, and measures are defined and specified exclusively top-down in OGSM. OKRs are set top-down and bottom-up by the teams.
- ⚡ Cadence: OGSM sets long-term goals – annually and/or for three to five years. Regular reviews are not provided. OKRs are set for three to four months and reviewed in weekly check-ins.
- ⚡ Access: OGSM planning is prepared entirely by management and only communicated to the workforce in final form for implementation. OKRs are usually created transparently as well as team-oriented and are visible to all.
- 🤝 Action orientation: Although both frameworks do not provide concrete actions per se, they can easily be expanded to include initiatives (OKRs) and actions (OGSM).
- ⚡ Ambition: OKRs are always ambitious and failure is seen as an opportunity to learn and grow. OGSM also sets ambitious goals, but expects them to be achievable nonetheless.
- ⚡ Leadership: OGSM sees leaders in a rather authoritarian and controlling role. In the context of OKRs, they take a more coaching approach and focus on the potential of their employees.
- ⚡ Adaptability: OGSMs are usually created annually and adapted from time to time. In extreme cases, the plan does not change at all. OKRs, on the other hand, are very flexible, are usually prepared on a quarterly basis, and are checked regularly.
OGSM and OKRs – still a good combination?
Despite or perhaps because of all these differences, OKRs can be a useful complement to the OGSM model. Used together, OKRs within a more long-term OGSM planning framework provide the ability to place temporary emphasis on specific issues or goals and to focus on specific strategies for a short period of time with additional OKRs.
Additionally, in doing so, OKRs complement bottom-up elements that are inherently missing from the OGSM model and shift the focus away from strong, authoritarian leadership and toward autonomy, alignment, and collaboration.
So, in summary, combining OGSM and OKRs offers organizations the opportunity to keep long-term goals and metrics in mind, while still remaining flexible and adaptable along the way, empowering their employees and providing a contemporary way of working.
💡 By the way, there are other strategic frameworks that can promote a company's success through strategic goals. In addition to OGSM and OKR, it's also worth taking a look at MBO, Hoshin Kanri, and Balanced Scorecard.
Conclusion: long-term planning with OGSM, short-term flexibility with OKRs
In summary, organizations can plan very well for the long term in the OGSM format – but quickly reach their limits when conditions in the market or within the company change at short notice. To counteract this, it can make sense to combine OGSM with other, more short-term methods for strategic management.
As is often the case in management, a closer look at OGSM reveals that there is no single optimal approach. Each method is suitable for different purposes and comes with its own strengths and weaknesses.
A mix of methods – for example OGSM and OKRs – can help to balance these weaknesses and to approach the optimal solution individually.